what causes not able to get full breath
Shortness of breath—what doctors call dyspnea—is the unpleasant awareness of having difficulty breathing. People experience and describe shortness of jiff differently depending on the cause.
The charge per unit and depth of breathing unremarkably increase during do and at loftier altitudes, just the increase seldom causes discomfort. Animate rate is as well increased at residuum in people with many disorders, whether of the lungs or other parts of the body. For example, people with a fever generally exhale faster.
With dyspnea, faster breathing is accompanied by the awareness of running out of air. People experience every bit if they cannot breathe fast enough or deeply plenty. They may notice that more than endeavour is needed to expand the chest when breathing in or to expel air when breathing out. They may also have the uncomfortable sensation that inhaling (inspiration) is urgently needed before exhaling (expiration) is completed and have diverse sensations oft described equally tightness in the chest.
The most common causes overall include
-
Physical deconditioning (for example, weakening of muscles and the heart due to inactivity)
-
Weight gain
-
Pregnancy
The most common crusade in people with a chronic lung or heart disorder is
-
Worsening of their illness
Even so, such people may also develop another disorder. For instance, people with long-standing asthma may have a heart set on, or people with chronic heart failure may develop pneumonia.
People who accept lung disorders oft experience dyspnea when they physically exert themselves. During practise, the body makes more carbon dioxide and uses more than oxygen. The respiratory center in the encephalon speeds up breathing when blood levels of oxygen are low or blood levels of carbon dioxide are high. If the center or lungs are not functioning unremarkably, even a little exertion can dramatically increase the breathing rate and dyspnea. Dyspnea is so unpleasant that people avoid exertion. As the lung disorder becomes more than astringent, dyspnea may occur even at residual.
Dyspnea may result from
-
Restrictive lung disorders
-
Obstructive lung disorders
In obstructive disorders (such every bit COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Chronic obstructive pulmonary illness is persistent narrowing (blocking, or obstacle) of the airways occurring with emphysema, chronic obstructive bronchitis, or both disorders. Cigarette... read more 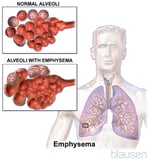 or asthma Asthma Asthma is a condition in which the airways narrow—unremarkably reversibly—in response to certain stimuli. Coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath that occur in response to specific triggers are... read more than
or asthma Asthma Asthma is a condition in which the airways narrow—unremarkably reversibly—in response to certain stimuli. Coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath that occur in response to specific triggers are... read more than 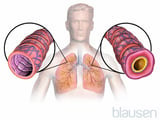 ), resistance to airflow is increased because the airways are narrowed. Because airways widen during inhalation, air can usually exist pulled in. However, because airways narrow during exhalation, air cannot exist exhaled from the lungs as fast every bit normal, and people wheeze and animate is labored. Dyspnea results when too much air is left in the lungs after exhaling.
), resistance to airflow is increased because the airways are narrowed. Because airways widen during inhalation, air can usually exist pulled in. However, because airways narrow during exhalation, air cannot exist exhaled from the lungs as fast every bit normal, and people wheeze and animate is labored. Dyspnea results when too much air is left in the lungs after exhaling.
People with asthma have dyspnea when they have an assault. Doctors typically advise people to continue an inhaler on paw to use during an attack. The drug in the inhaler helps open the airways.
Some people with heart failure have orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, or both. Orthopnea is shortness of jiff that occurs when people lie down and is relieved by sitting up. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea is a sudden, oft terrifying attack of dyspnea during sleep. People awaken gasping and must sit or stand to catch their breath. This disorder is an extreme form of orthopnea and a sign of severe heart failure.
In hyperventilation syndrome, people feel that they cannot become enough air, and they exhale heavily and speedily. This syndrome is commonly acquired past anxiety rather than a physical problem. Many people who experience it are frightened, may have breast pain, and may believe they are having a eye attack. They may have a change in consciousness, usually described equally feeling that events occurring around them are far away, and they may feel tingling in their hands and anxiety and effectually their oral fissure.
The following information can help people decide whether a doctor's evaluation is needed and help them know what to expect during the evaluation.
In people with dyspnea, the following symptoms are of particular business concern:
-
Shortness of breath at remainder
-
A decreased level of consciousness, agitation, or confusion
-
Chest discomfort or the feeling the heart is pounding or racing or has skipped a trounce (palpitations)
-
Weight loss
-
Night sweats
People who have shortness of breath at rest, chest hurting, palpitations, a decreased level of consciousness, agitation, or confusion or accept difficulty moving air in or out of their lungs should become to the hospital right away. Such people may need immediate testing, treatment, and sometimes access to the hospital. Other people should call a doctor. The doctor can determine how rapidly they need to be evaluated based on the nature and severity of their symptoms, their age, and whatever underlying medical weather condition. Typically, they should be evaluated inside a few days.
Doctors ask questions to make up one's mind
-
When shortness of jiff started
-
Whether information technology started abruptly or gradually
-
How long the person has felt short of jiff
-
Whether any conditions (such as common cold, exertion, exposure to allergens, or lying downwards) trigger it or make it worse
The person is as well asked questions about past medical history (including whatsoever lung or heart disorders), a history of smoking, whatever family members who take had high claret pressure or high cholesterol levels, and risk factors for pulmonary embolism (such as recent hospitalization, surgery, or long-distance travel).
The physical exam focuses on the heart and lungs. Doctors listen to the lungs for congestion, wheezing, and abnormal sounds called crackles. They heed to the heart for murmurs (suggesting a heart valve disorder). Swelling of both legs suggests heart failure, merely swelling of only one leg is more likely to outcome from a claret clot in the leg. A blood clot in the leg may break off and travel to the claret vessels in the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism.
Handling of dyspnea is directed at the cause. People with a low blood oxygen level are given supplemental oxygen using plastic nasal prongs or a plastic mask worn over the face. In astringent cases, particularly if people cannot exhale deeply or rapidly enough, breathing may be assisted by mechanical ventilation using a breathing tube inserted in the windpipe or a tight-fitting confront mask.
Morphine may be given intravenously to reduce anxiety and the discomfort of dyspnea in people with diverse disorders, including a heart attack, pulmonary embolism, and a concluding illness.
-
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is commonly acquired by lung or heart disorders.
-
In people with a chronic lung disorder (such as chronic obstructive pulmonary affliction) or heart disorder (such equally heart failure), the almost common cause of dyspnea is a flare-up of the chronic disorder, but these people tin can also develop a new problem (such as a middle attack) that contributes to or causes dyspnea.
-
People who have dyspnea at remainder, a decreased level of consciousness, or confusion should go to the hospital immediately for emergency evaluation.
-
To determine the severity of the problem, doctors measure oxygen levels in the blood with a sensor placed on a finger (pulse oximetry).
-
Doctors evaluate people for inadequate delivery of claret and oxygen to the heart (myocardial ischemia) and for pulmonary embolism, but sometimes symptoms of these disorders are vague.
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/lung-and-airway-disorders/symptoms-of-lung-disorders/shortness-of-breath
Belum ada Komentar untuk "what causes not able to get full breath"
Posting Komentar